When it comes to cloud computing solutions, there are two main options: public cloud and private cloud.
The cloud service option you choose will depend mainly on your business needs. For example, you may consider a private cloud if you want high security and performance. But a public cloud could be your go-to if you need a budget-friendly and scalable cloud solution.
Curious to learn more?
We’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of both types of cloud. Then, we’ll look at the factors to consider when choosing between the two services to help you select the best fit for your business.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- What is a public cloud?
- What is a private cloud?
- Difference between private and public cloud
- Advantages of public clouds
- Disadvantages of public clouds
- Advantages of private clouds
- Disadvantages of private clouds
- Factors to consider when choosing between a public and private cloud
- Public cloud vs. private cloud: Which one should you use?
What is a public cloud?
A public cloud is where a third-party cloud service provider (CSP) offers cloud services and resources through the internet to multiple organizations.
The CSP uses groups of data centers divided into virtual machines, which different organizations share. As a client, you can use these virtual machines by renting them out. You can also pay for additional cloud-based services like software applications or storage.
In some cases, the cloud provider offers these services using a subscription model, such as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), or software-as-a-service (SaaS).
Examples of public cloud providers include Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure.
What is a private cloud?

A private cloud, also called an on-premises data center, is a cloud computing model where a single organization has exclusive access to cloud services, resources, and infrastructure.
Just like with a public cloud, a CSP may offer private cloud technology. The difference is that, unlike the resources of a public cloud, which multiple organizations share, the resources of a private cloud are dedicated to one company.
Private clouds are ideal for highly-regulated businesses, such as hospitals, financial institutions, and government agencies.
These organizations require customizable and secure IT environments since they manage sensitive data like customers’ personal and medical records. They also handle confidential information that needs additional security to prevent leaks or cybercriminal attacks.
Liquid Web is an example of a company that offers private cloud services.
Difference between private and public cloud
The main difference between public and private cloud deployments is that public clouds use shared infrastructure, divided up for multiple clients, while private clouds use a company's own or dedicated infrastructure.
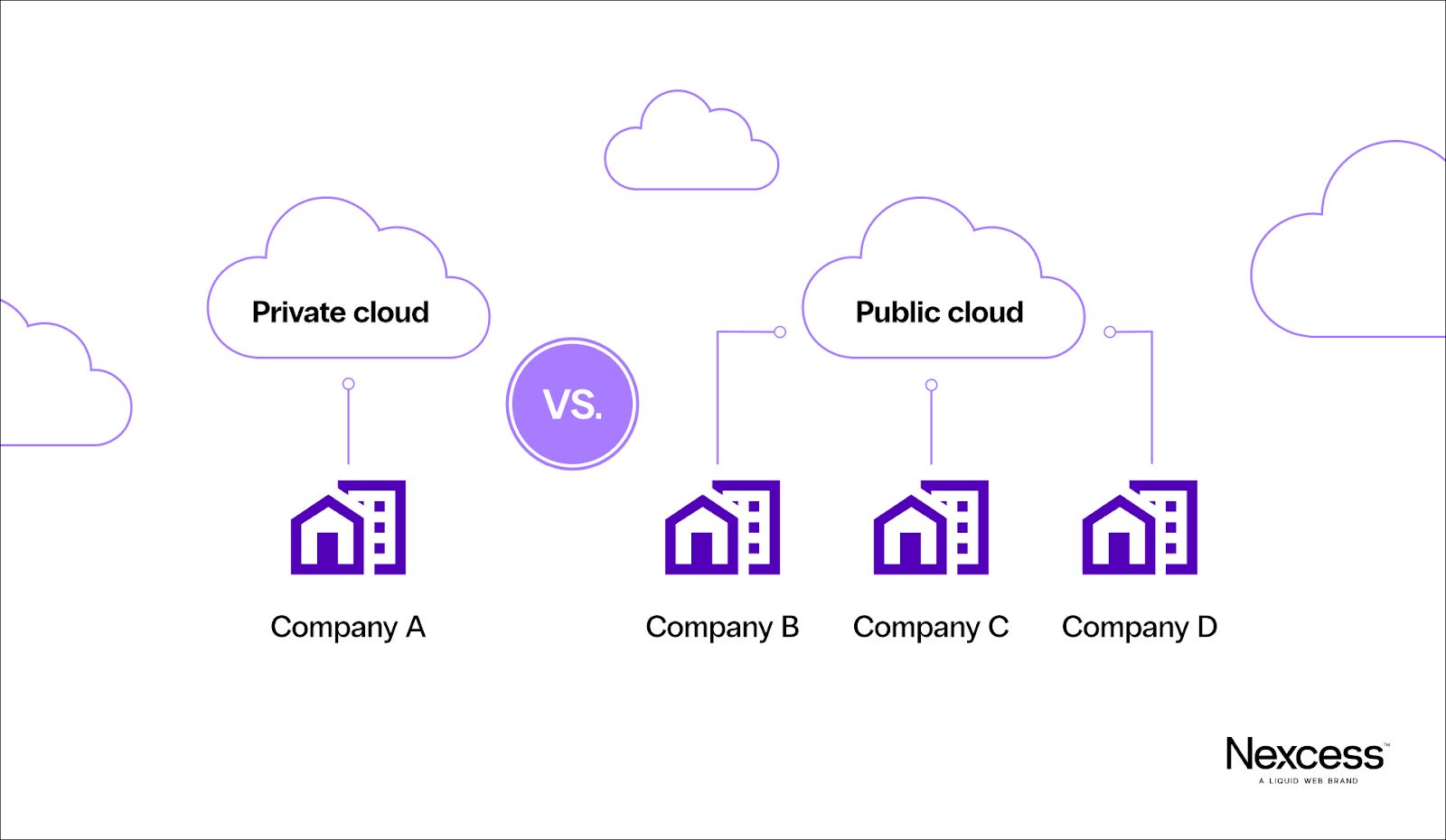
We can compare a public cloud to renting an apartment, while a private cloud is like renting a house.
The house gives you more privacy, but it costs more to rent it. Maintaining the home can also be a bit expensive since you have to hire a contractor for maintenance — or do it yourself.
In contrast, renting an apartment is cheaper, and the property manager handles the regular maintenance. However, you have to share the building with other tenants, meaning there’s less space and privacy.
Hybrid cloud vs. multi-cloud
A hybrid cloud model combines a public and private cloud. In contrast, a multi-cloud environment combines two or more public clouds but doesn't integrate private cloud or on-premises infrastructure.
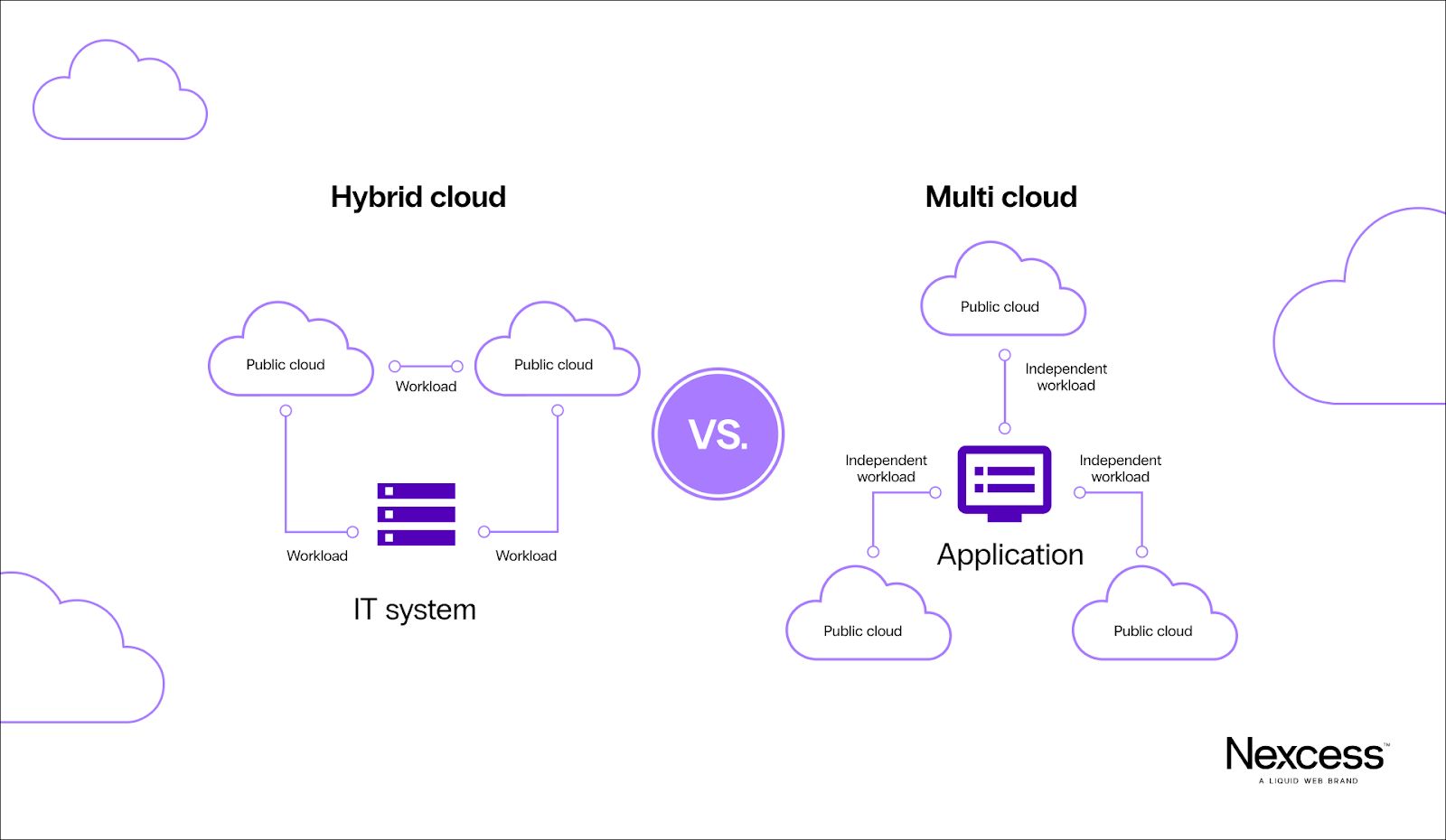
The main reason your enterprise might opt for a hybrid cloud is so you can use the public cloud for data and workloads that aren’t sensitive but deploy the private cloud for sensitive data.
For example, the public cloud can be ideal for low-risk activities, such as hosting web-based applications like email. Meanwhile, you can reserve the private cloud for functions that need greater security, such as storing personal data or payment processing.
That way, your enterprise is able to maintain a higher level of security for specific functions while benefiting from the cost savings of a public cloud.
The key benefit of using a multi-cloud strategy is backup and disaster recovery. Even if tragedy strikes one cloud provider, your business’s applications can continue running on another vendor’s platform.
Advantages of public clouds
Gartner estimates that global spending on public cloud services will grow by 20.7 percent to reach $591.8 billion in 2023, up from $490.3 billion in 2022. These forecasts indicate that the demand for public cloud services is growing.
That being the case, let's look at the main advantages of public cloud solutions to understand why you may also want to move your enterprise’s storage and workloads to public cloud platforms.
Public clouds are more cost-effective
One of the main advantages of using a public cloud is that the cloud service provider manages the hardware, application, and bandwidth for you. This means that you don't incur any initial investment costs and won't need to train IT personnel to monitor and maintain the system.
Moreover, public cloud services often use a pay-as-you-go model, so you make monthly or annual payments based on how you use the resources. As a result, you can run web applications without committing to fixed costs for software, servers, or maintenance.
Public clouds are highly scalable
Another benefit of using a public cloud is you can scale it to fit dynamic market conditions or changing business needs.
Since the CSP allocates resources between customers dynamically, you can double or even triple your storage or computing resources to meet peak demand. You’re also able to achieve this without exponentially increasing the system's cost.
The cloud service provider manages maintenance
Your CSP maintains all the infrastructure needed to operate the system, including power, cooling systems, and redundant components.
In other words, you don't have to worry about updating the infrastructure or aspects like upgrades and security. You also need minimal IT staff to run the system, reducing overall costs.
Public clouds are more reliable
Since public clouds support multiple businesses, their resources are distributed across various servers. If one cloud server fails, your applications can switch to another server automatically.
As a result, you can reduce the length of downtime your company’s website experiences, which could lead to a poor customer experience and a loss of revenue.
Disadvantages of public clouds
Although a public cloud offers businesses several benefits, it also poses some challenges to organizations. It’s important that you’re familiar with these to understand whether a public cloud is right for your enterprise.
Public clouds have more security and privacy concerns
Security and privacy of data continue to be the top two concerns for many businesses. Data breaches in the third quarter of 2022 exposed approximately 15 million data records globally. This was a 37 percent rise in data breaches compared to the previous quarter.

Although public cloud services offered by leading vendors are secure, the real challenge comes from companies that don’t use the system securely.
When another firm misuses the public cloud’s infrastructure or doesn’t follow security best practices, it might put your enterprise’s data at risk since a successful breach on the main server could expose every other server to cybercriminal attacks.
Advantages of private clouds
The International Data Corporation (IDC) reports that the dedicated cloud infrastructure segment rose by 25.3 percent to reach $7.1 billion in the third quarter of 2022.
This indicates that corporations are pivoting toward adopting private cloud services, either in addition to their public cloud services or in place of them.
With that in mind, let’s look at some ways your enterprise might benefit from using private clouds.
Private clouds offer increased privacy and security
One of the key advantages that a private cloud offers enterprises is security and privacy.
A private cloud runs on specific physical machines and is hosted on data centers that are owned or rented by a single organization. This makes it much easier to track and enhance a private cloud’s physical security.
Private clouds are also more secure than public clouds since you can only access them through private network links instead of the internet. As a result, only authorized users can access private cloud applications.
Private clouds offer high performance
Private infrastructure constantly offers high performance with improved speed and space since it caters to a single tenant. That means the system can satisfy even a large enterprise’s computation and storage requirements.
Private clouds are more customizable
Since public clouds support many businesses, they often lock clients into preset security practices and network setups. With a private cloud environment, you’re the only customer, so you can tailor the system to your business needs rather than the other way around.
Private clouds also offer you more flexibility with virtualization, which enables multiple operating systems and apps to run on the same physical machine and adjust resources to meet the requirements of each application.
As a result, you can allocate disk space, CPU, and RAM resources as you need them and scale them up and down based on your business’s requirements.
Private clouds offer improved regulatory compliance

As we previously mentioned, institutions with compliance requirements often prefer a private cloud environment due to its security and privacy benefits.
Also, CSPs offering hosted private clouds can help you address significant compliance elements such as PCI compliance and HIPAA compliant hosting.
Disadvantages of private clouds
Although a private cloud offers benefits such as high security and performance, it also has its share of drawbacks.
Here are some disadvantages of investing in a private cloud.
Private clouds are expensive
Deploying a private cloud on-site will cost you more than if you were to host your applications using public cloud architecture. You must invest in network infrastructure, servers, software licenses, and data centers.
That being said, managed private cloud hosting solutions like Liquid Web provide a cost-effective alternative without upfront investment. The platform helps you scale your business and access top-tier hosting infrastructure without thinking about the complexities of a data center.
Private clouds require significant IT resources
On top of being capital intensive, maintaining a private cloud will cost your enterprise more than if you opted for a public cloud environment.
Naturally, you'll require IT personnel to deploy, configure, and manage both your cloud’s software and hardware.
Private clouds can have reliability issues
Private cloud hosting is only as reliable as your software, hardware, and IT staff. If anything were to happen (like server failure or a power outage), you'd be responsible for fixing it. As a result, you have to invest more money in additional redundancy measures to ensure your systems are reliable.
In contrast, large public cloud vendors design their technology to be redundant and have dedicated personnel whose job it is to troubleshoot outages at no expense to the client.
Factors to consider when choosing between a public and private cloud
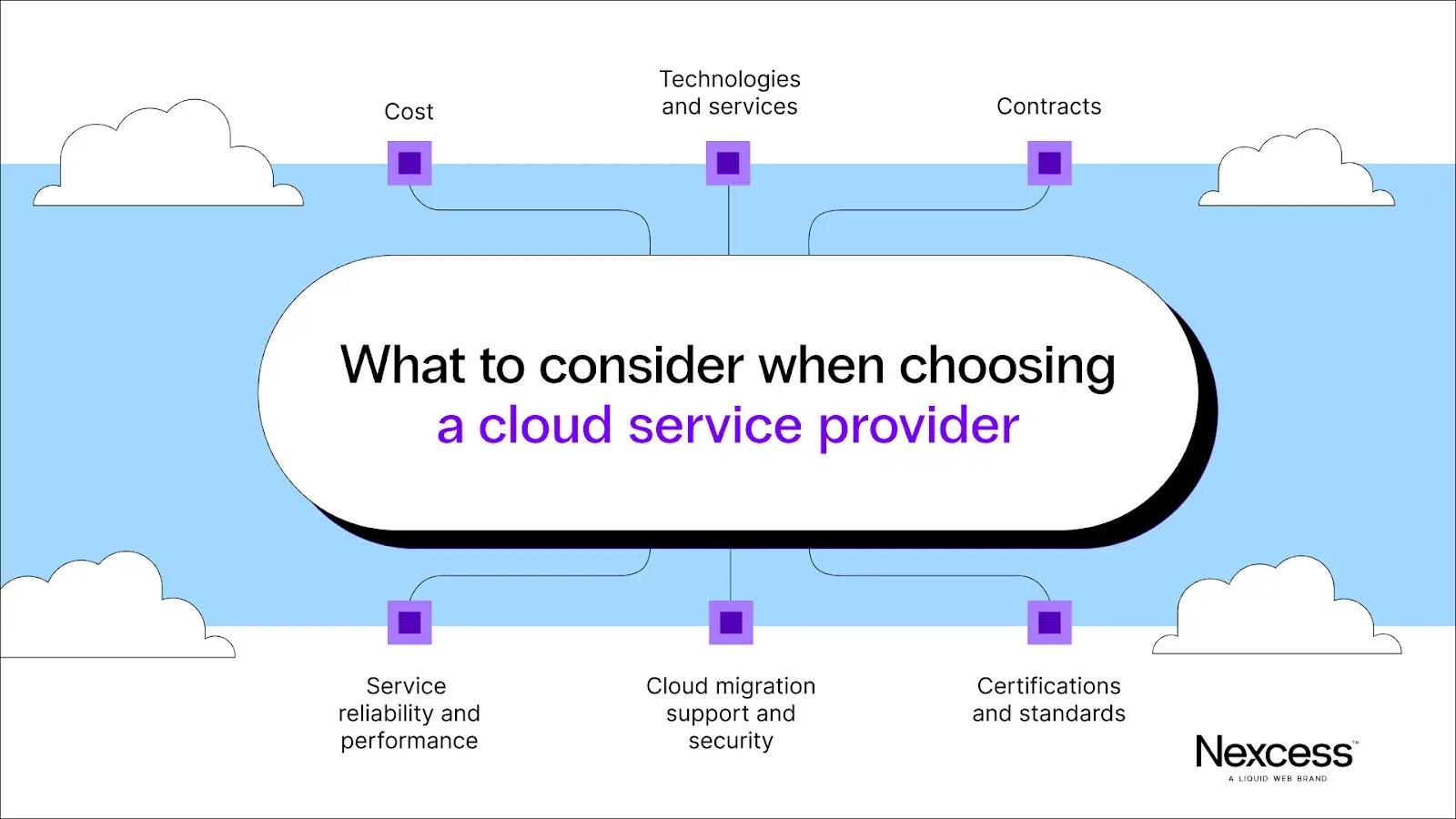
Picking the best cloud computing service for your business depends on several factors.
For example, what kind of data do you work with? How fast do you want to be able to access that data? Do you plan on expanding your database? With the right information, you'll know which cloud strategy is better, more cost-effective, and more flexible.
Here are four factors to consider when looking for a cloud solution for your company.
1. Cloud security and compliance
A public cloud offers security through SSL, firewalls, and other security measures. However, a private cloud will help you actively restrict internal and external access to your data centers, allowing only authorized users to access the system.
Supposing your company handles highly-sensitive information, such as financial, medical, or governmental data, you’d likely want the extra physical security that comes with an on-premises solution rather than a public cloud.
But if your company mostly runs an ecommerce store that handles general data, you may want to outsource that part of your business to a public cloud hosting provider.
2. Performance needs
A private cloud is typically used by one company, so the infrastructure is reserved and dedicated to that organization alone. Therefore, it offers the best performance in terms of cloud computing and faster access to devices and data.
In contrast, a public cloud supports multiple businesses at the same time, so the performance depends on your cloud service provider’s efficiency.
If your enterprise deals with scientific, financial, or big data applications, then you’d probably want to use a private cloud that provides the lowest possible latencies. But if your business uses apps that don’t need a lot of bandwidth, then a public cloud is a cost-effective solution.
3. Scalability requirements
A public cloud can scale up and down as needed since the vendors have the available servers. They can even do it automatically, so the available storage will scale based on your business needs. That can be beneficial if you plan to expand your database or deal with volatile data streams.
On the other hand, scaling an on-premises private cloud requires more hardware, which can be expensive and time-consuming. As a result, if you want maximum elasticity from your platform, a public cloud service may be the better option.
4. Available budget
Installing on-premises infrastructure requires significant investment in hardware and software. It also requires employees to operate, manage, and maintain the system, which can be costly.
In contrast, public clouds are cost-effective since you don't have to make this initial investment. A public cloud service provider will also likely employ a pay-what-you-use billing model, where you pay for the resources as you go.
With that in mind, you may want to consider using public cloud resources if you have a fixed budget.
Public cloud vs. private cloud: Which one should you use?
Choosing between a public and private cloud depends on your company's requirements, goals, and budget. While a public cloud provides scalability and affordability, private clouds offer greater security and customizability.
Ultimately, the best cloud service option will be the one that meets your unique business needs.
At Nexcess, we offer flexible managed cloud hosting plans to our customers. By providing cloud solutions that scale with your business, we ensure you get the performance, storage, and security you need without asking you to compromise on cost.
Contact us today to learn more about how Nexcess can help support the growth of your enterprise.

